Gibbs Free Energy - Questions
The Gibbs Free Energy Concept Builder is comprised of 16 multi-part, numerical questions spread across three difficulty levels. Students will receive one question for each difficulty level. Questions involve the completion of a table. The Concept Builder is coded to select at random a question for each level.
The three Difficulty Levels in this Concept Builder differ only in terms of the complexity of the thermodchemical equations and the complexity of the given numbers. Here is the breakdown of the levels:
- Apprentice Difficulty Level: Questions 1-4 ... Students complete a 4-row table with the ultimate goal in each row of determining the ∆G value and deciding on the spontaneity of the reaction. The calculations are guided.
- Master Difficulty Level: Questions 5-10 ... Students complete a 5-row table to determine the ∆G value and the spontaneity of the reaction. Each calculation involves the same process with different numbers.
- Wizard Difficulty Level: Questions 11-16 ... Students complete a 5-row table to determine an unknown quantity - ∆H, ∆S, ∆G, or temperature.
The questions from each group are shown below. Teachers are encouraged to view the questions in order to judge which difficulty levels are most appropriate for their classes. Alternatively, teachers can do the
Concept Builder to gain a feel for the student experience..
The Physics Classroom grants teachers and other users the right to print these questions for private use. Users are also granted the right to copy the text and modify it for their own use. However, this document should not be uploaded to other servers for distribution to and/or display by others. The Physics Classroom website should remain the only website or server from which the document is distributed or displayed. We also provide a PDF that teachers can use under the same conditions. We have included a link to the PDF near the bottom of this page.
Gibb's Free Energy
Apprentice Difficulty Level
Question 1
Consider: N2(g) + O2(g) ==> 2 NO(g)
for which. ΔH = +180.5 kJ and. ΔS = +421.5 J/K
Use the enthalpy change and entropy change values to complete the table:
Question 2
Consider: N2(g) + O2(g) ==> 2 NO(g)
for which. ΔH = +180.5 kJ and. ΔS = +421.5 J/K
Use the enthalpy change and entropy change values to complete the table:
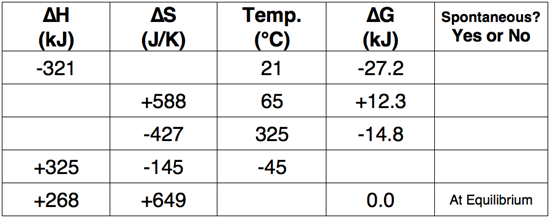
Question 3
Consider: CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g)
for which. ΔH = +178.3 kJ and ΔS = +160.5 J/K
Use the enthalpy change and entropy change values to complete the table.
Question 4
Consider: CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g)
for which. ΔH = +178.3 kJ and ΔS = +160.5 J/K
Use the enthalpy change and entropy change values to complete the table.
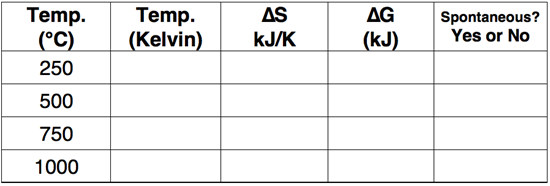
Master Difficulty Level
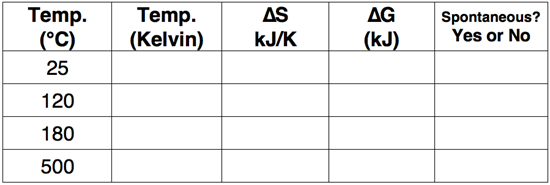
Question 5
Use the Gibb's Free Energy equation to complete the following table.

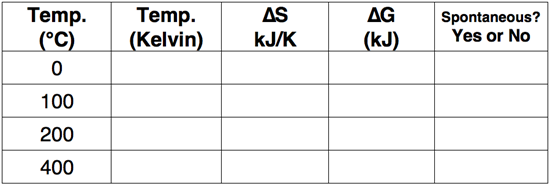
Question 6
Use the Gibb's Free Energy equation to complete the following table.
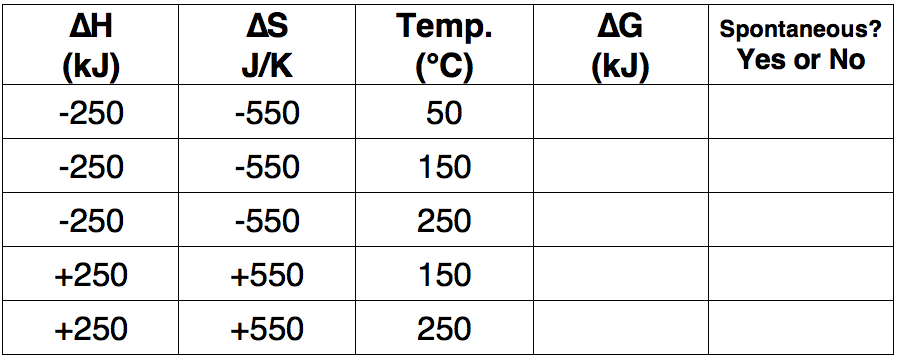
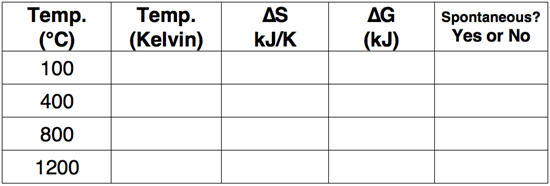
Question 7
Use the Gibb's Free Energy equation to complete the following table.
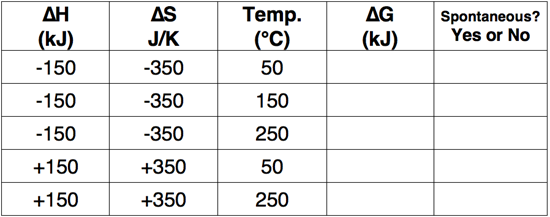
Question 8
Use the Gibb's Free Energy equation to complete the following table.
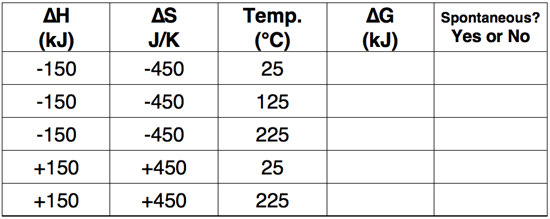
Question 9
Use the Gibb's Free Energy equation to complete the following table.
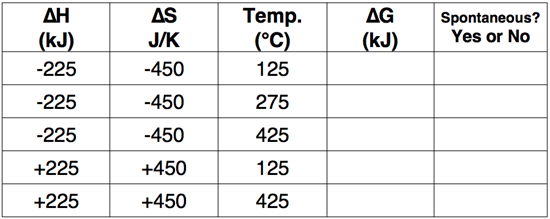
Question 10
Use the Gibb's Free Energy equation to complete the following table.
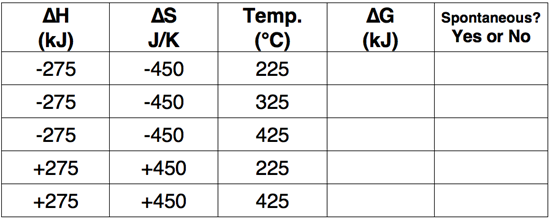
Wizard Difficulty Level
Question 11
Use the Gibb's Free Energy equation to complete the following table.
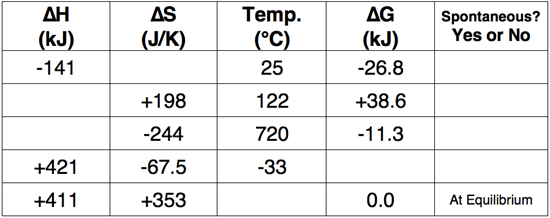
Question 12
Use the Gibb's Free Energy equation to complete the following table.
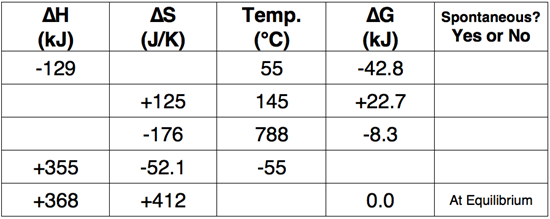
Question 13
Use the Gibb's Free Energy equation to complete the following table.
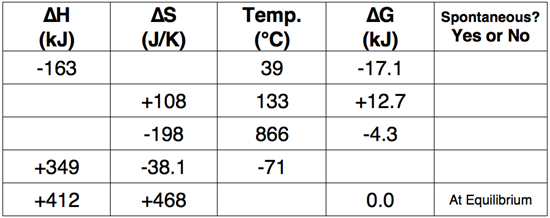
Question 14
Use the Gibb's Free Energy equation to complete the following table.
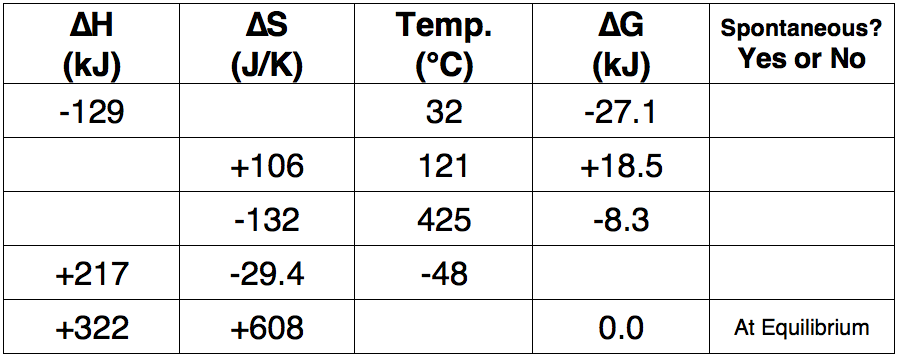
Question 15
Use the Gibb's Free Energy equation to complete the following table.
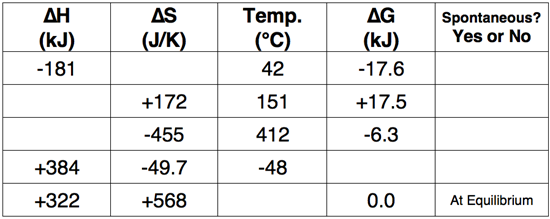
Question 16
Use the Gibb's Free Energy equation to complete the following table.