Bernoulli's Principle - Questions
The Bernoulli's Principle Concept Builder is comprised of 38 questions. The questions are divided into 16 different question groups and spread across three different activities. Questions in the same group are rather similar to one another. The Concept Builder is coded to select at random a question from each group until a student is successful with that group of questions.
The questions and question groups are organized into three different activities. The activities are differentiated as follows:
- Bernoulli Effects Question Groups 1-6: Students analyze six common examples of the Bernoulli effect (airplane wing, spinning golf ball, spinning baseball, etc.) and use Bernoulli's principle to determine where the pressure is greatest and predict the effect that this has upon the object.
- Pressure Meters Question Groups 7-10: Students analyze fluid flow in a horizontal tube that narrows or widens in order to identify the location with the greatest speed and the location with the greatest pressure. They match their findings to a diagram displaying a set of attached Venturi tubes or a manometer.
- Bernoulli Thinking Question Groups 11-16: Students use Bernoulli's equation (and the continuity equation) to compare the velocity, height, and pressure at two locations along an ascending or descending flow tube.
The questions from each group are shown below. Teachers are encouraged to view the questions in order to judge which activity is most appropriate for their classes. We recommend doing all three activities.
The Physics Classroom grants teachers and other users the right to print these questions for private use. Users are also granted the right to copy the text and modify it for their own use. However, this document should not be uploaded to other servers for distribution to and/or display by others. The Physics Classroom website should remain the only website or server from which the document is distributed or displayed. We also provide a PDF that teachers can use under the same conditions. We have included a link to the PDF near the bottom of this page.
Bernoulli's Principle
Activity 1: Bernoulli Effects
Question Group 1
Question 1

The profile of an airplane wing is shown. Air approaching the wing flows over the top and bottom of the wing.
Air flowing around the wing will be moving faster at location ______.
The pressure of the air on the wing will be greatest at location _______.
The result is that ______.
a. there will be a net upward force on the wing.
b. there will be a net downward force on the wing.
c. the wing will be under severe stress and at risk of collapse.
Question 2
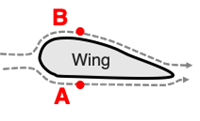
The profile of an airplane wing is shown. Air approaching the wing flows over the top and bottom of the wing.
Air flowing around the wing will be moving faster at location ______.
The pressure of the air on the wing will be greatest at location _______.
The result is that ______.
a. there will be a net upward force on the wing, lifting the airplane.
b. there will be a net downward force on the wing, lowering the airplane.
c. the wing will be under severe stress and at risk of collapse.
Question Group 2
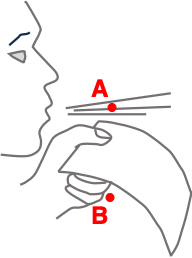 Question 3
Question 3
During a Physics lab, a student holds a sheet of paper in front of her lips. She directs a steady stream of air across the top of the paper.
The air speed will be greatest at location ______.
The pressure of the air will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. there will be a net upward force on the paper, raising the paper
b. there will be a net downward force on the paper, pushing it more downward
c. the paper will begin flapping wildly and likely be torn into shreads
Question 4
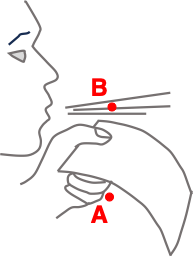
During a Physics lab, a student holds a sheet of paper in front of her lips. She directs a steady stream of air across the top of the paper.
The air speed will be greatest at location ______.
The pressure of the air will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. there will be a net upward force on the paper, raising the paper
b. there will be a net downward force on the paper, pushing it more downward
c. the paper will begin flapping wildly and likely be torn into shreads
Question Group 3
 Question 5
Question 5
Two toy boats are placed side-by-side in a shallow tank of water. Water from a hose is directed between the boats.
The water speed will be greatest at location ______.
The water pressure will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. the boats will move closer together.
b. the boats will move further apart.
c. the walls of the tank will be under stress and at risk of collapse.
 Question 6
Question 6
Two toy boats are placed side-by-side in a shallow tank of water. Water from a hose is directed between the boats.
The water speed will be greatest at location ______.
The water pressure will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. the boats will move closer together.
b. the boats will move further apart.
c. the walls of the tank will be under stress and at risk of collapse.
 Question 7
Question 7
Two toy boats are placed side-by-side in a shallow tank of water. Water from a hose is directed between the boats.
The water speed will be greatest at location ______.
The water pressure will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. the boats will move closer together.
b. the boats will move further apart.
c. the walls of the tank will be under stress and at risk of collapse.
 Question 8
Question 8
Two toy boats are placed side-by-side in a shallow tank of water. Water from a hose is directed between the boats.
The water speed will be greatest at location ______.
The water pressure will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. the boats will move closer together.
b. the boats will move further apart.
c. the walls of the tank will be under stress and at risk of collapse.
Question Group 4
 Question 9
Question 9
A spinning baseball is moving to the right through the air. Its spin direction is shown. Air flows around the top and bottom of the ball.
The air speed will be greatest at location ______.
The pressure of the air will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. the ball will sink downward (relative to its projectile path)
b. the ball will rise upward (relative to its projectile path)
c. blur excessively due to its spin, causing the batter to lose sight of it
 Question 10
Question 10
A spinning baseball is moving to the left through the air. Its spin direction is shown. Air flows around the top and bottom of the ball. The air speed will be greatest at location ______.
The pressure of the air will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. the ball will sink downward (relative to its projectile path)
b. the ball will rise upward (relative to its projectile path)
c. blur excessively due to its spin, causing the batter to lose sight of it
 Question 11
Question 11
A spinning baseball is moving to the right through the air. Its spin direction is shown. Air flows around the top and bottom of the ball.
The air speed will be greatest at location ______.
The pressure of the air will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. the ball will sink downward (relative to its projectile path)
b. the ball will rise upward (relative to its projectile path)
c. blur excessively due to its spin, causing the batter to lose sight of it
 Question 12
Question 12
A spinning baseball is moving to the left through the air. Its spin direction is shown. Air flows around the top and bottom of the ball.
The air speed will be greatest at location ______.
The pressure of the air will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. the ball will sink downward (relative to its projectile path)
b. the ball will rise upward (relative to its projectile path)
c. blur excessively due to its spin, causing the batter to lose sight of it
Question Group 5
 Question 13
Question 13
A spinning golf ball is moving to the right through the air. Its spin direction is shown. Air flows around the sides of the ball.
The air speed will be greatest at location ______.
The pressure of the air will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. the ball will follow a path similar to path 1
b. the ball will follow a path similar to path 2
c. the ball will oscillate back and forth between paths 1 and 2
 Question 14
Question 14
A spinning golf ball is moving to the left through the air. Its spin direction is shown. Air flows around the sides of the ball.
The air speed will be greatest at location ______.
The pressure of the air will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. the ball will follow a path similar to path 1
b. the ball will follow a path similar to path 2
c. the ball will oscillate back and forth between paths 1 and 2
 Question 15
Question 15
A spinning golf ball is moving to the right through the air. Its spin direction is shown. Air flows around the sides of the ball.
The air speed will be greatest at location ______.
The pressure of the air will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. the ball will follow a path similar to path 1
b. the ball will follow a path similar to path 2
c. the ball will oscillate back and forth between paths 1 and 2
 Question 16
Question 16
A spinning golf ball is moving to the left through the air. Its spin direction is shown. Air flows around the sides of the ball.
The air speed will be greatest at location ______.
The pressure of the air will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. the ball will follow a path similar to path 1
b. the ball will follow a path similar to path 2
c. the ball will oscillate back and forth between paths 1 and 2
Question Group 6
 Question 17
Question 17
Strong winds during a tornado cause air to flow around the top and sides of an unvented house.
The air speed will be greatest at location ______.
The pressure of the air will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. the roof will be at risk of being lifted off the home
b. the roof will be secured tightly to the home
c. the contents of the home will blow out the windows
 Question 18
Question 18
Strong winds during a tornado cause air to flow around the top and sides of an unvented house.
The air speed will be greatest at location ______.
The pressure of the air will be greatest at location ______.
The result is that ______.
a. the roof will be at risk of being lifted off the home
b. the roof will be secured tightly to the home
c. the contents of the home will blow out the windows
Activity 2: Pressure Meters
Question Group 7
 Question 19
Question 19
Fluid in a pipe flows between regions with different cross-sectional areas. Venturi meters are used to measure the relative fluid pressure at A and B. Tap on the diagram that shows the proper Venturi meter readings.
The fluid velocity is greatest at ________.
The fluid pressure is greatest at ________.
 Question 20
Question 20
Fluid in a pipe flows between regions with different cross-sectional areas. Venturi meters are used to measure the relative fluid pressure at A and B. Tap on the diagram that shows the proper Venturi meter readings.
The fluid velocity is greatest at ________.
The fluid pressure is greatest at ________.
Question Group 8
 Question 21
Question 21
Fluid in a pipe flows between regions with different cross-sectional areas. Venturi meters are used to measure the relative fluid pressure at A and B. Tap on the diagram that shows the proper Venturi meter readings.
The fluid velocity is greatest at ________.
The fluid pressure is greatest at ________.
 Question 22
Question 22
Fluid in a pipe flows between regions with different cross-sectional areas. Venturi meters are used to measure the relative fluid pressure at A and B. Tap on the diagram that shows the proper Venturi meter readings.
The fluid velocity is greatest at ________.
The fluid pressure is greatest at ________.
Question Group 9
 Question 23
Question 23
Air in a pipe flows between regions with different cross-sectional areas. Manometers are used to measure the relative fluid pressure at A and B. Tap on the diagram that shows the proper manometer readings.
The fluid velocity is greatest at ________.
The fluid pressure is greatest at ________.
 Question 24
Question 24
Air in a pipe flows between regions with different cross-sectional areas. Manometers are used to measure the relative fluid pressure at A and B. Tap on the diagram that shows the proper manometer readings.
The fluid velocity is greatest at ________.
The fluid pressure is greatest at ________.
Question Group 10
 Question 25
Question 25
Air in a pipe flows between regions with different cross-sectional areas. Manometers are used to measure the relative fluid pressure at A and B. Tap on the diagram that shows the proper manometer readings.
The fluid velocity is greatest at ________.
The fluid pressure is greatest at ________.
 Question 26
Question 26
Air in a pipe flows between regions with different cross-sectional areas. Manometers are used to measure the relative fluid pressure at A and B. Tap on the diagram that shows the proper manometer readings.
The fluid velocity is greatest at ________.
The fluid pressure is greatest at ________.
Activity 3: Bernoulli Thinking
Question Group 11
 Question 27
Question 27
A fluid is undergoing steady-state laminar flow through a pipe. Two locations - 1 and 2 - are identified on the diagram.
Use Bernoulli’s equation to indicate how the pressure, velocity, and height for locations 1 and 2 compare to one another. Answer options are 1 = 2, 1 > 2, 1 < 2, and not enough information.
Question 28
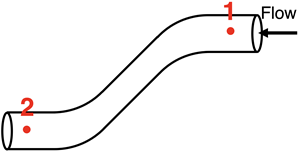
A fluid is undergoing steady-state laminar flow through a pipe. Two locations - 1 and 2 - are identified on the diagram.
Use Bernoulli’s equation to indicate how the pressure, velocity, and height for locations 1 and 2 compare to one another. Answer options are 1 = 2, 1 > 2, 1 < 2, and not enough information.
Question Group 12
 Question 29
Question 29
A fluid is undergoing steady-state laminar flow through a pipe. Two locations - 1 and 2 - are identified on the diagram.
Use Bernoulli’s equation to indicate how the pressure, velocity, and height for locations 1 and 2 compare to one another. Answer options are 1 = 2, 1 > 2, 1 < 2, and not enough information.
 Question 30
Question 30
A fluid is undergoing steady-state laminar flow through a pipe. Two locations - 1 and 2 - are identified on the diagram.
Use Bernoulli’s equation to indicate how the pressure, velocity, and height for locations 1 and 2 compare to one another. Answer options are 1 = 2, 1 > 2, 1 < 2, and not enough information.
Question Group 13
 Question 31
Question 31
A fluid is undergoing steady-state laminar flow through a pipe. Two locations - 1 and 2 - are identified on the diagram.
Use Bernoulli’s equation to indicate how the pressure, velocity, and height for locations 1 and 2 compare to one another. Answer options are 1 = 2, 1 > 2, 1 < 2, and not enough information.
 Question 32
Question 32
A fluid is undergoing steady-state laminar flow through a pipe. Two locations - 1 and 2 - are identified on the diagram.
Use Bernoulli’s equation to indicate how the pressure, velocity, and height for locations 1 and 2 compare to one another. Answer options are 1 = 2, 1 > 2, 1 < 2, and not enough information.
Question Group 14
 Question 33
Question 33
A fluid is undergoing steady-state laminar flow through a pipe. Two locations - 1 and 2 - are identified on the diagram.
Use Bernoulli’s equation to indicate how the pressure, velocity, and height for locations 1 and 2 compare to one another. Answer options are 1 = 2, 1 > 2, 1 < 2, and not enough information.
 Question 34
Question 34
A fluid is undergoing steady-state laminar flow through a pipe. Two locations - 1 and 2 - are identified on the diagram.
Use Bernoulli’s equation to indicate how the pressure, velocity, and height for locations 1 and 2 compare to one another. Answer options are 1 = 2, 1 > 2, 1 < 2, and not enough information.
Question Group 15
 Question 35
Question 35
A fluid is undergoing steady-state laminar flow through a pipe. Two locations - 1 and 2 - are identified on the diagram.
Use Bernoulli’s equation to indicate how the pressure, velocity, and height for locations 1 and 2 compare to one another. Answer options are 1 = 2, 1 > 2, 1 < 2, and not enough information.
 Question 36
Question 36
A fluid is undergoing steady-state laminar flow through a pipe. Two locations - 1 and 2 - are identified on the diagram.
Use Bernoulli’s equation to indicate how the pressure, velocity, and height for locations 1 and 2 compare to one another. Answer options are 1 = 2, 1 > 2, 1 < 2, and not enough information.
Question Group 16
 Question 37
Question 37
A fluid is undergoing steady-state laminar flow through a pipe. Two locations - 1 and 2 - are identified on the diagram.
Use Bernoulli’s equation to indicate how the pressure, velocity, and height for locations 1 and 2 compare to one another. Answer options are 1 = 2, 1 > 2, 1 < 2, and not enough information.
 Question 38
Question 38
A fluid is undergoing steady-state laminar flow through a pipe. Two locations - 1 and 2 - are identified on the diagram.
Use Bernoulli’s equation to indicate how the pressure, velocity, and height for locations 1 and 2 compare to one another. Answer options are 1 = 2, 1 > 2, 1 < 2, and not enough information.