Equilibrium
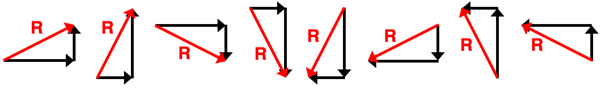
The Equilibrium Concept Builder includes 36 questions organized into 12 Question Groups and spread across three difficulty levels. Each question involves the same task - add an east-west vector and a north-south vector to an object so that it is in a state of equilibrium. Questions in the same difficulty level include the same number of given vectors. Questions in the same Question Group are very similar, having the same number of given vectors to be balanced and having those vectors in the same quadrants.
The three difficulty levels are differentiated as follows:
- Apprentice Difficulty Level Questions 1-4: A single vector is given. The vector makes an angle to the traditional coordinate axes. Students must add an E/W vector and a N/S vector to balance the force.
- Master DifficultyLevel Questions 5-8: Two vectors are given. The vectors make an angle to the traditional coordinate axes. Students must add an E/W vector and a N/S vector to balance the forces.
- Wizard Difficulty Level Questions 9-12: Three vectors are given. The vectors make an angle to the traditional coordinate axes. Students must add an E/W vector and a N/S vector to balance the forces.
The Physics Classroom grants teachers and other users the right to print these questions for private use. Users are also granted the right to copy the text and modify it for their own use. However, this document nor its graphics should not be uploaded to other servers for distribution to and/or display by others. The Physics Classroom website should remain the only website or server from which the document and its graphics is distributed or displayed. We also provide a PDF that teachers can use under the same conditions. We have included a link to the PDF near the bottom of this page.
Equilibrium
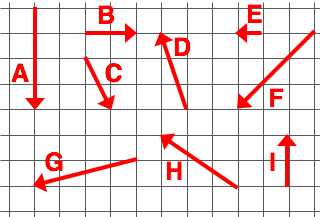
The following diagram is used in all questions:
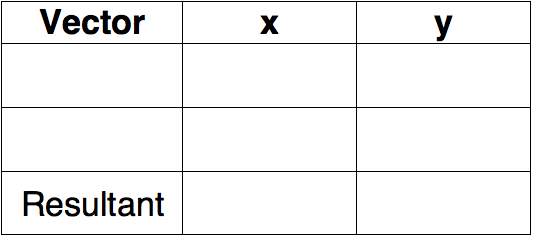
Question Groups 1-3 all use the following table:
Question Group 1
Question 1
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 5 km along its edge
D + G = ???
Question 2
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 10 km along its edge
D + G = ???
Question 3
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 20 km along its edge
D + G = ???
Question Group 2
Question 4
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 5 km along its edge
H + F = ???
Question 5
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 10 km along its edge
H + F = ???
Question 6
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 20 km along its edge
H + F = ???
Question Group 3
Question 7
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 5 km along its edge
C + G = ???
Question 8
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 10 km along its edge
C + G = ???
Question 9
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 20 km along its edge
C + G = ???
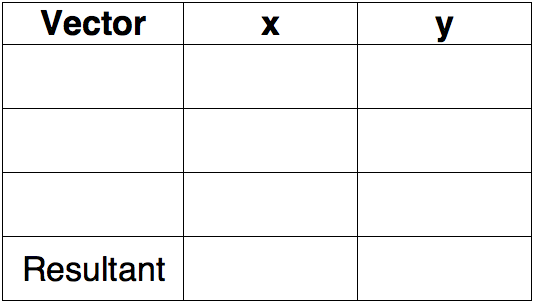
Question Groups 4-6 all use the following table:
Question Group 4
Question 10
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 5 km along its edge
B + C + G = ???
Question 11
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 10 km along its edge
B + C + G = ???
Question 12
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 20 km along its edge
B + C + G = ???
Question Group 5
Question 13
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 5 km along its edge
H + F + I = ???
Question 14
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 10 km along its edge
H + F + I = ???
Question 15
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 20 km along its edge
H + F + I = ???
Question Group 6
Question 16
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 5 km along its edge
A + F + D = ???
Question 17
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 10 km along its edge
A + F + D = ???
Question 18
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 20 km along its edge
A + F + D = ???
Question Groups 7-9 all use the following table:
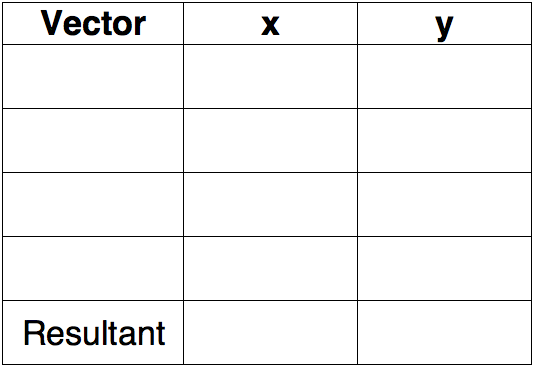
Question Group 7
Question 19
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 5 km along its edge
A + H + C + D = ???
Question 20
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 10 km along its edge
A + H + C + D = ???
Question 21
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 20 km along its edge
A + H + C + D = ???
Question Group 8
Question 22
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 5 km along its edge
H + B + G + I = ???
Question 23
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 10 km along its edge
H + B + G + I = ???
Question 24
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 20 km along its edge
H + B + G + I = ???
Question Group 9
Question 25
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 5 km along its edge
F + D + C + B = ???
Question 26
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 10 km along its edge
F + D + C + B = ???
Question 27
Use the diagram and scale to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the vector addition equation. Begin with the table.
Scale: 1 square = 20 km along its edge
F + D + C + B = ???
The following graphic appears on all questions: