Hold down the T key for 3 seconds to activate the audio accessibility mode, at which point you can click the K key to pause and resume audio. Useful for the Check Your Understanding and See Answers.
 According to Newton's third law, for every action force there is an equal (in size) and opposite (in direction) reaction force. Forces always come in pairs - known as "action-reaction force pairs." Identifying and describing action-reaction force pairs is a simple matter of identifying the two interacting objects and making two statements describing who is pushing on whom and in what direction. For example, consider the interaction between a baseball bat and a baseball.
According to Newton's third law, for every action force there is an equal (in size) and opposite (in direction) reaction force. Forces always come in pairs - known as "action-reaction force pairs." Identifying and describing action-reaction force pairs is a simple matter of identifying the two interacting objects and making two statements describing who is pushing on whom and in what direction. For example, consider the interaction between a baseball bat and a baseball.
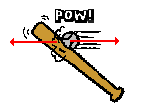
The baseball forces the bat to the left; the bat forces the ball to the right. Together, these two forces exerted upon two different objects form the action-reaction force pair. Note that in the description of the two forces, the nouns in the sentence describing the forces simply switch places.
Consider the following three examples. One of the forces in the mutual interaction is described; describe the other force in the action-reaction force pair. Click the button to view the answer.
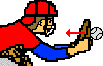
Baseball pushes glove leftwards.
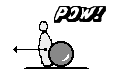
Bowling ball pushes pin leftwards.

Enclosed air particles push balloon wall outwards.
Check Your Understanding
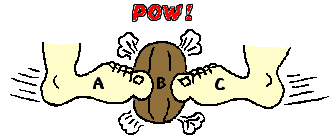
1. Consider the interaction depicted below between foot A, ball B, and foot C. The three objects interact simultaneously (at the same time). Identify the two pairs of action-reaction forces. Use the notation "foot A", "foot C", and "ball B" in your statements. Click the button to view the answer.
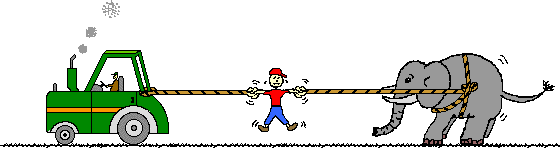
2. Identify at least six pairs of action-reaction force pairs in the following diagram.